RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
38 CANCER CONTROL 2021
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
04/02/19 04/07/19 01/12/19 29/04/20 26/09/20 23/02/21 23/07/21 20/12/21
Data sets
2 4
14
80
0
20
40
60
80
100
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Percentage of registries
Data completeness
Surgery (81/114)
22
13
84
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
Surgical procedure (63/81 )
5 8
15
71
Radiotherapy (73/114)
5 8
15
71
Chemotherapy (73/114)
16
6
14
64
HER-2 status (64/114)
37
6
21
37
BRCA1/2 (19/114)
13
3
16
67
ER/PR (61/114)
9
16
25
51
Ki67 (35/114)
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
Less than
25%
25-49%5
0-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
administrative problems have
arisen, both at the London
School of Hygiene and Tropical
Medicine (LSHTM) and among
cancer registries around the
world.
One of the most important
features of this ERC
consolidator grant, offering
financial support to cancer
registries in LMICs, has turned
out to be more difficult than we
expected, due to the need to
set up legal contracts between
LSHTM and each registry
or its host institution. Other
difficulties have arisen because
English is not the mother tongue
for most of our colleagues
in LMICs, and because it has
proved impossible for some
cancer registries even to open
a bank account, or if that is
achieved, to receive financial
support from another country,
in this case the United Kingdom.
The United Kingdom's exit
from the European Union
(EU) also did not help. In many
European countries, where
the General Data Protection
Regulation (GDPR) was already
mis-interpreted or overinterpreted by
administrators,
it has become much more difficult to obtain essential data for
research, e.g., full dates of birth, diagnosis or last known vital
status. Similar regulations have created problems in releasing
detailed data in North America.
Despite the difficulties posed by the COVID-19 pandemic
and by Brexit, we have finalised the legal contracts to permit
the transfer of funds for data collection to selected cancer
registries in LMICs, and data-sharing agreements with cancer
registries in the 27 EU Member States to enable transmission
of sensitive personal data in compliance with the EU GDPR.
Nevertheless, this was an extremely time-consuming exercise.
Unless cancer control policies are to be based on statistical
projections from data that are scanty or of average quality, or
even, where data are non-existent, modelled on the basis of
untestable assumptions from data collected in other countries,
action is urgently required to create population-based cancer
planning appropriate cancer control strategies to guarantee
equal access to cancer prevention, screening and treatment to
women in every country in the world.
The evidence from this research will help drive policy to
reduce inequalities in survival from the most common cancers
in women. This work will involve targeted dissemination of
the findings to scientists, policymakers, cancer patients and
the general public. Results from VENUSCANCER will also
be used by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and
Development (OECD) in its Health at a Glance series, and for
the WHO Global Breast Cancer Initiative.
COVID-19 pandemic: ethical, legal and
administrative issues
The COVID-19 pandemic of 2020-2021 has changed many
aspects of our lives, including research. Many technical and
0
20
40
60
80
100
04/02/19 04/07/19 01/12/19 29/04/20 26/09/20 23/02/21 23/07/21 20/12/21
Data sets
2 4
14
80
0
20
40
60
80
100
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Percentage of registries
Data completeness
Surgery (81/114)
22
13
84
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
Surgical procedure (63/81 )
5 8
15
71
Radiotherapy (73/114)
5 8
15
71
Chemotherapy (73/114)
16
6
14
64
HER-2 status (64/114)
37
6
21
37
BRCA1/2 (19/114)
13
3
16
67
ER/PR (61/114)
9
16
25
51
Ki67 (35/114)
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
0
20
40
60
80
100
Percentage of registries
Less than
25%
25-49% 50-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
Less than
25%
25-49%5
0-74% 75-100%
Data completeness
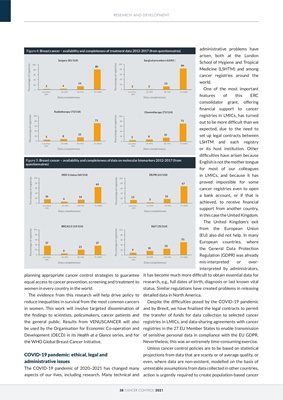
Figure 4: Breast cancer - availability and completeness of treatment data 2012-2017 (from questionnaires)
Figure 5: Breast cancer - availability and completeness of data on molecular biomarkers 2012-2017 (from
questionnaires)