evidence on the economics of AGP use in the livestock
industry and the potential economic consequences for
producers and consumers of phasing out AGPs.
‰ The growth response to Antimicrobial Growth Promoters
(AGPs) is small in optimized production systems
The discovery that antimicrobials fed in sub-therapeutic
concentrations to livestock can hasten their growth and
prevent disease came just as farmers in the United States
were struggling to keep pace with demand for food and
animal protein (27,28). Antimicrobial use for growth
promotion and disease prevention soon became an integral
part of a new agricultural production model, despite early
warnings about the potential risks of developing resistance
(29).
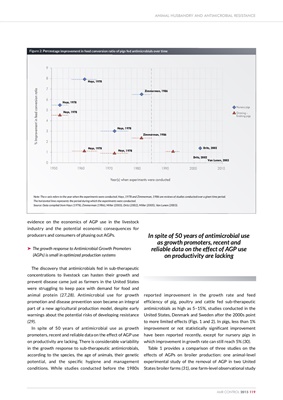
In spite of 50 years of antimicrobial use as growth
promoters, recent and reliable data on the effect of AGP use
on productivity are lacking. There is considerable variability
in the growth response to sub-therapeutic antimicrobials,
according to the species, the age of animals, their genetic
potential, and the specific hygiene and management
conditions. While studies conducted before the 1980s
reported improvement in the growth rate and feed
efficiency of pig, poultry and cattle fed sub-therapeutic
antimicrobials as high as 5-15%, studies conducted in the
United States, Denmark and Sweden after the 2000s point
to more limited effects (Figs. 1 and 2). In pigs, less than 1%
improvement or not statistically significant improvement
have been reported recently, except for nursery pigs in
which improvement in growth rate can still reach 5% (30).
Table 1 provides a comparison of three studies on the
effects of AGPs on broiler production: one animal-level
experimental study of the removal of AGP in two United
States broiler farms (31), one farm-level observational study
ANIMAL HUSBANDRY AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE
AMR CONTROL 2015 119
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Year(s) when experiments were conducted
% Improvement in feed conversion ratio
1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Nursery pigs
Growing -
finishing pigs
Hays, 1978
Hays, 1978
Hays, 1978
Zimmerman, 1986
Dritz, 2002
Dritz, 2002 Van Lunen, 2003
Hays, 1978
Hays, 1978
Hays, 1978
Zimmerman, 1986
Figure 2: Percentage improvement in feed conversion ratio of pigs fed antimicrobials over time
Note: The x-axis refers to the year when the experiments were conducted. Hays, 1978 and Zimmerman, 1986 are reviews of studies conducted over a given time period.
The horizontal lines represents the period during which the experiments were conducted.
Source: Data compiled from Hays (1978), Zimmerman (1986), Miller (2003), Dritz (2002), Miller (2005), Van Lunen (2003).
In spite of 50 years of antimicrobial use
as growth promoters, recent and
reliable data on the effect of AGP use
on productivity are lacking