MONITORING, SURVEILLANCE AND NATIONAL PLANS
AMR CONTROL 2015 49
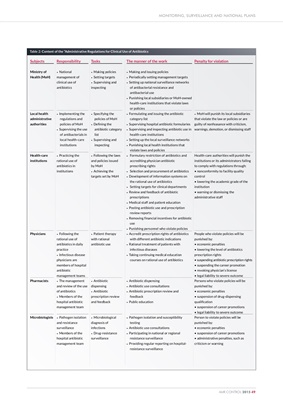
Table 2: Content of the "Administrative Regulations for Clinical Use of Antibiotics
Subjects
Ministry of
Health (MoH)
Local health
administrative
authorities
Health-care
institutions
Physicians
Pharmacists
Microbiologists Responsibility
• National
management of
clinical use of
antibiotics
• Implementing the
regulations and
policies of MoH
• Supervising the use
of antibacterials in
local health-care
institutions
• Practicing the
rational use of
antibiotics in
institutions
• Following the
rational use of
antibiotics in daily
practice
• Infectious disease
physicians are
members of hospital
antibiotic
management teams
• The management
and review of the use
of antibiotics
• Members of the
hospital antibiotic
management team
• Pathogen isolation
and resistance
surveillance
• Members of the
hospital antibiotic
management team
Tasks
• Making policies
• Setting targets
• Supervising and
inspecting
• Specifying the
policies of MoH
• Defining the
antibiotic category
list
• Supervising and
inspecting
• Following the laws
and policies issued
by MoH
• Achieving the
targets set by MoH
• Patient therapy
with rational
antibiotic use
• Antibiotic
dispensing
• Antibiotic
prescription review
and feedback
• Microbiological
diagnosis of
infections
• Drug-resistance
surveillance
The manner of the work
• Making and issuing policies
• Periodically setting management targets
• Setting up national surveillance networks
of antibacterial resistance and
antibacterial use
• Punishing local subsidiaries or MoH-owned
health-care institutions that violate laws
or policies
• Formulating and issuing the antibiotic
category list
• Supervising hospital antibiotic formularies
• Supervising and inspecting antibiotic use in
health-care institutions
• Setting up the local surveillance networks
• Punishing local health institutions that
violate laws and policies
• Formulary restriction of antibiotics and
accrediting physician antibiotic
prescribing rights
• Selection and procurement of antibiotics
• Development of information systems on
the rational use of antibiotics
• Setting targets for clinical departments
• Review and feedback of antibiotic
prescriptions
• Medical staff and patient education
• Posting antibiotic use and prescription
review reports
• Removing financial incentives for antibiotic
use
• Punishing personnel who violate policies
• Accredit prescription rights of antibiotics
with different antibiotic indications
• Rational treatment of patients with
infectious diseases
• Taking continuing medical education
courses on rational use of antibiotics
• Antibiotic dispensing
• Antibiotic use consultations
• Antibiotic prescription review and
feedback
• Public education
• Pathogen isolation and susceptibility
testing
• Antibiotic use consultations
• Participating in national or regional
resistance surveillance
• Providing regular reporting on hospitalresistance
surveillance
Penalty for violation
• MoH will punish its local subsidiaries
that violate the law or policies or are
guilty of nonfeasance with criticism,
warnings, demotion, or dismissing staff
Health-care authorities will punish the
institutions or its administrators failing
to comply with regulations through:
• nonconformity to facility quality
control
• lowering the academic grade of the
institution
• warning or dismissing the
administrative staff
People who violate policies will be
punished by:
• economic penalties
• lowering the level of antibiotics
prescription rights
• suspending antibiotic prescription rights
• suspending the career promotion
• revoking physician's license
• legal liability to severe outcome
Persons who violate policies will be
punished by:
• economic penalties
• suspension of drug-dispensing
qualification
• suspension of career promotions
• legal liability to severe outcome
Person to violate policies will be
punished by:
• economic penalties
• suspension of career promotions
• administrative penalties, such as
criticism or warning