national core standards has been developed for both AMS
and IPC to ensure a standardized approach. Every institution
will have an AMR committee and AMS team(s) to effect good
practice and oversee appropriate antimicrobial prescribing.
Optimization of surveillance and early detection of
AMR
Surveillance of four components of AMR is to be
strengthened within the strategy framework:
‰ Antimicrobial resistance patterns;
‰ Antimicrobial consumption;
‰ Antimicrobial drug quality;
‰ Medication errors.
A centralized data warehouse (CDW) will collate public
and private national resistance data. Specific drug resistance
patterns are to become statutorily notifiable. This will
include both statutory notifications of resistance patterns
for common bacterial infections that are already at high
prevalence such as methicillin resistant Staphylococcus
aureus (MRSA) and extended spectrum beta-lactamase
(ESBL) producing bacteria, and sentinel notification of the
most serious resistant MDR bacteria currently at low
prevalence, e.g. carbapenemase-producing Gram-negative
MONITORING, SURVEILLANCE AND NATIONAL PLANS
AMR CONTROL 2015 57
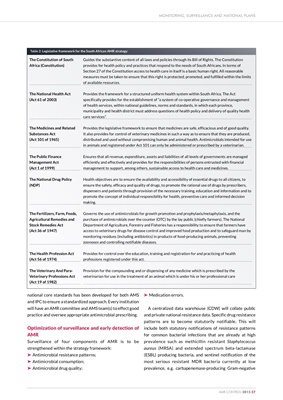
Table 2: Legislative framework for the South African AMR strategy
The Constitution of South
Africa (Constitution)
The National Health Act
(Act 61 of 2003)
The Medicines and Related
Substances Act
(Act 101 of 1965)
The Public Finance
Management Act
(Act 1 of 1999)
The National Drug Policy
(NDP)
The Fertilizers, Farm, Feeds,
Agricultural Remedies and
Stock Remedies Act
(Act 36 of 1947)
The Health Profession Act
(Act 56 of 1974)
The Veterinary And ParaVeterinary
Professions Act
(Act 19 of 1982)
Guides the substantive content of all laws and policies through its Bill of Rights. The Constitution
provides for health policy and practices that respond to the needs of South Africans. In terms of
Section 27 of the Constitution access to health care in itself is a basic human right. All reasonable
measures must be taken to ensure that this right is protected, promoted, and fulfilled within the limits
of available resources.
Provides the framework for a structured uniform health system within South Africa. The Act
specifically provides for the establishment of "a system of co-operative governance and management
of health services, within national guidelines, norms and standards, in which each province,
municipality and health district must address questions of health policy and delivery of quality health
care services".
Provides the legislative framework to ensure that medicines are safe, efficacious and of good quality.
It also provides for control of veterinary medicines in such a way as to ensure that they are produced,
distributed and used without compromising human and animal health. Antimicrobials intended for use
in animals and registered under Act 101 can only be administered or prescribed by a veterinarian.
Ensures that all revenue, expenditure, assets and liabilities of all levels of governments are managed
efficiently and effectively and provides for the responsibilities of persons entrusted with financial
management to support, among others, sustainable access to health care and medicines.
Health objectives are to ensure the availability and accessibility of essential drugs to all citizens, to
ensure the safety, efficacy and quality of drugs, to promote the rational use of drugs by prescribers,
dispensers and patients through provision of the necessary training, education and information and to
promote the concept of individual responsibility for health, preventive care and informed decision
making.
Governs the use of antimicrobials for growth promotion and prophylaxis/metaphylaxis, and the
purchase of antimicrobials over the counter (OTC) by the lay public (chiefly farmers). The National
Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries has a responsibility to ensure that farmers have
access to veterinary drugs for disease control and improved food production and to safeguard man by
monitoring residues (including antibiotics) in products of food-producing animals, preventing
zoonoses and controlling notifiable diseases.
Provides for control over the education, training and registration for and practicing of health
professions registered under this act.
Provision for the compounding and or dispensing of any medicine which is prescribed by the
veterinarian for use in the treatment of an animal which is under his or her professional care