year to be allocated to all countries, according to needs,
under an agreement that they would monitor use and
restrict utilization to agreed health-care settings (such as
secondary or tertiary level hospitals, for example).
This would exclude direct commercialization of the
product in private pharmacies and prescription for
indications where other therapeutic interventions are
available. These conditions would ensure preservation of the
new drugs.
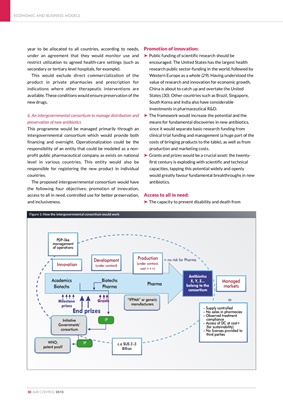
6. An intergovernmental consortium to manage distribution and
preservation of new antibiotics
This programme would be managed primarily through an
intergovernmental consortium which would provide both
financing and oversight. Operationalization could be the
responsibility of an entity that could be modeled as a nonprofit
public pharmaceutical company as exists on national
level in various countries. This entity would also be
responsible for registering the new product in individual
countries.
The proposed intergovernmental consortium would have
the following four objectives: promotion of innovation,
access to all in need, controlled use for better preservation,
and inclusiveness.
Promotion of innovation:
‰ Public funding of scientific research should be
encouraged. The United States has the largest health
research public sector-funding in the world, followed by
Western Europe as a whole (29). Having understood the
value of research and innovation for economic growth,
China is about to catch up and overtake the United
States (30). Other countries such as Brazil, Singapore,
South Korea and India also have considerable
investments in pharmaceutical R&D.
‰ The framework would increase the potential and the
means for fundamental discoveries in new antibiotics,
since it would separate basic research funding from
clinical trial funding and management (a huge part of the
costs of bringing products to the table), as well as from
production and marketing costs.
‰ Grants and prizes would be a crucial asset: the twentyfirst
century is exploding with scientific and technical
capacities, tapping this potential widely and openly
would greatly favour fundamental breakthroughs in new
antibiotics.
Access to all in need:
‰ The capacity to prevent disability and death from
ECONOMIC AND BUSINESS MODELS
30 AMR CONTROL 2015
PDP-like
management
of operations
- Supply controlled
- No sales in pharmacies
- Observed treatment
compliance
- Access of DC at cost+
(for sustainability)
- No licenses provided to
third parties
Innovation
Development
(under contract)
Managed
markets
Production
(under contract,
cost +++)
c.a $US 2-3
Billion
WHO;
patent pool?
Initiative
Governments'
consortium
"IFPMA" or generic
manufacturers
Academics
Biotechs
Biotechs
Pharma
Pharma
IP
IP
Antibiotics
X, Y, Z...
belong to the
consortium
= no risk for Pharma
Milestone
prizes
Grants
End prizes
=
Figure 1: How the intergovernmental consortium would work