28 LV= Annual Report 2012
Principal risks and uncertainties
A common risk categorisation basis is used across LV= to ensure a consistent record of the names,
descriptions and structure of the group’s risks. The principal risks to which LV= is exposed are shown below:
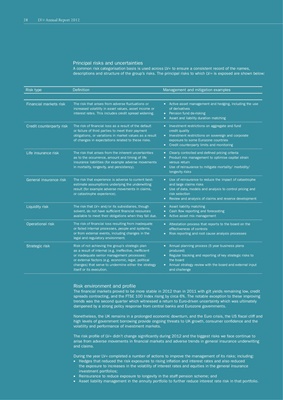
Risk type Definition Management and mitigation examples
Financial markets risk The risk that arises from adverse fluctuations or l Active asset management and hedging, including the use
increased volatility in asset values, asset income or of derivatives
interest rates. This includes credit spread widening. l Pension fund de-risking
l Asset and liability duration matching
Credit counterparty risk The risk of financial loss as a result of the default l Investment restrictions on aggregate and fund
or failure of third parties to meet their payment credit quality
obligations, or variations in market values as a result l Investment restrictions on sovereign and corporate
of changes in expectations related to these risks. exposure to some Eurozone countries
l Credit counterparty limits and monitoring
Life insurance risk The risk that arises from the inherent uncertainties l Clearly controlled and defined pricing criteria
as to the occurrence, amount and timing of life l Product mix management to optimise capital strain
insurance liabilities (for example adverse movements versus return
in mortality, longevity, and persistency). l Use of reinsurance to mitigate mortality/ morbidity/
longevity risks
General insurance risk The risk that experience is adverse to current best- l Use of reinsurance to reduce the impact of catastrophe
estimate assumptions underlying the underwriting and large claims risks
result (for example adverse movements in claims, l Use of data, models and analysis to control pricing and
or catastrophe experience). risk selection
l Review and analysis of claims and reserve development
Liquidity risk The risk that LV= and/or its subsidiaries, though l Asset liability matching
solvent, do not have sufficient financial resources l Cash flow reporting and forecasting
available to meet their obligations when they fall due. l Active asset mix management
Operational risk The risk of financial loss resulting from inadequate l Attestation process that reports to the board on the
or failed internal processes, people and systems, effectiveness of controls
or from external events, including changes in the l Risk reporting and root cause analysis processes
legal and regulatory environment.
Strategic risk Risk of not achieving the group’s strategic plan l Annual planning process (5 year business plans
as a result of internal (e.g. ineffective, inefficient produced)
or inadequate senior management processes) l Regular tracking and reporting of key strategic risks to
or external factors (e.g. economic, legal, political the board
changes) that serve to undermine either the strategy l Annual strategy review with the board and external input
itself or its execution. and challenge
Risk environment and profile
The financial markets proved to be more stable in 2012 than in 2011 with gilt yields remaining low, credit
spreads contracting, and the FTSE 100 Index rising by circa 6%. The notable exception to these improving
trends was the second quarter which witnessed a return to Euro-driven uncertainty which was ultimately
dampened by a strong policy response from central banks and Eurozone governments.
Nonetheless, the UK remains in a prolonged economic downturn, and the Euro crisis, the US fiscal cliff and
high levels of government borrowing provide ongoing threats to UK growth, consumer confidence and the
volatility and performance of investment markets.
The risk profile of LV= didn’t change significantly during 2012 and the biggest risks we face continue to
arise from adverse movements in financial markets and adverse trends in general insurance underwriting
and claims.
During the year LV= completed a number of actions to improve the management of its risks; including:
l Hedges that reduced the risk exposures to rising inflation and interest rates and also reduced
the exposure to increases in the volatility of interest rates and equities in the general insurance
investment portfolios;
l Reinsurance to reduce exposure to longevity in the staff pension scheme; and
l Asset liability management in the annuity portfolio to further reduce interest rate risk in that portfolio.