Our Accounts 69
Notes to the Financial Statements continued
31 December 2012
3. Risk management and control (continued)
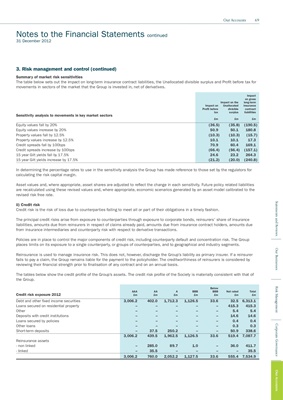
Summary of market risk sensitivities
The table below sets out the impact on long-term insurance contract liabilities, the Unallocated divisible surplus and Profit before tax for
movements in sectors of the market that the Group is invested in, net of derivatives.
Impact
on gross
Impact on the long-term
Impact on Unallocated insurance
Profit before divisible contract
tax surplus liabilities
Sensitivity analysis to movements in key market sectors
£m £m £m
Equity values fall by 20% (36.5) (35.8) (190.5)
Equity values increase by 20% 50.9 50.1 180.8
Property values fall by 12.5% (10.3) (10.3) (15.7)
Property values increase by 12.5% 10.1 10.1 17.3
Credit spreads fall by 100bps 70.9 60.4 169.1
Credit spreads increase by 100bps (66.4) (56.4) (157.1)
15 year Gilt yields fall by 17.5% 24.6 23.2 264.3
15 year Gilt yields increase by 17.5% (21.2) (20.0) (240.8)
In determining the percentage rates to use in the sensitivity analysis the Group has made reference to those set by the regulators for
calculating the risk capital margin.
Asset values and, where appropriate, asset shares are adjusted to reflect the change in each sensitivity. Future policy related liabilities
are recalculated using these revised values and, where appropriate, economic scenarios generated by an asset model calibrated to the
revised risk free rate.
Statements and Reviews
ii) Credit risk
Credit risk is the risk of loss due to counterparties failing to meet all or part of their obligations in a timely fashion.
The principal credit risks arise from exposure to counterparties through exposure to corporate bonds, reinsurers’ share of insurance
liabilities, amounts due from reinsurers in respect of claims already paid, amounts due from insurance contract holders, amounts due
from insurance intermediaries and counterparty risk with respect to derivative transactions.
Policies are in place to control the major components of credit risk, including counterparty default and concentration risk. The Group
places limits on its exposure to a single counterparty, or groups of counterparties, and to geographical and industry segments.
Our Businesses
Reinsurance is used to manage insurance risk. This does not, however, discharge the Group’s liability as primary insurer. If a reinsurer
fails to pay a claim, the Group remains liable for the payment to the policyholder. The creditworthiness of reinsurers is considered by
reviewing their financial strength prior to finalisation of any contract and on an annual basis.
The tables below show the credit profile of the Group’s assets. The credit risk profile of the Society is materially consistent with that of
the Group.
Risk Management
Below
AAA AA A BBB BBB Not rated Total
Credit risk exposure 2012 £m £m £m £m £m £m £m
Debt and other fixed income securities 3,006.2 402.0 1,712.3 1,126.5 33.6 32.5 6,313.1
Loans secured on residential property – – – – – 415.3 415.3
Other – – – – – 5.4 5.4
Deposits with credit institutions – – – – – 14.6 14.6
Loans secured by policies – – – – – 0.4 0.4
– – – – – 0.3 0.3
Corporate Governance
Other loans
Short-term deposits – 37.5 250.2 – – 50.9 338.6
3,006.2 439.5 1,962.5 1,126.5 33.6 519.4 7,087.7
Reinsurance assets
- non linked – 285.0 89.7 1.0 – 36.0 411.7
- linked – 35.5 – – – – 35.5
3,006.2 760.0 2,052.2 1,127.5 33.6 555.4 7,534.9
Our Accounts