REGIONAL INITIATIVES
obvious difference is seen in cancer of the cervix and breast. the best information possible is used in the development
Cervical cancer which occupied the top position among of cancer control programmes.
cancers in women in 1982 in most cities in India had been Based on the above, the yardsticks by which progress can be
replaced by breast cancer in all of the urban registries by measured will be:
2002, whereas the data from rural registries, although not ‰ The increase in survival rates of treated patients, based on
nearly as extensive, continues to be as before. It is therefore hospital series, reflecting the available infrastructure,
expected that the establishment of the TNCRP will usher in technology and trained personnel.
an era of knowledge acquisition on cancer patterns from all ‰ The improved survival of and relative proportions of
the districts of the state of Tamil Nadu, providing an atlas of treated and untreated patients observed in population
cancer that, if demonstrating clear regional differences will series, reflecting the accessibility to and/or development
be of great help in directing cancer control efforts. More of health services, referral and early detection practices.
directly, it is proposed to set up an early cancer detection ‰ The size of trends towards earlier stage of disease at
centre, including cancer education and awareness in all presentation, reflecting cancer awareness and education.
districts where the registry is collecting data. ‰ The establishment of prevention programmes and
demonstration of trends towards lower incidence rates,
Where are we in cancer control? with an emphasis on tobacco control.
In our perception, the most credible tools for the ‰ Accessibility and affordability of cancer care, which will
measurement of the success of cancer control programmes in reflect governmental commitment and public support.
a developing environment with limited resources will be:
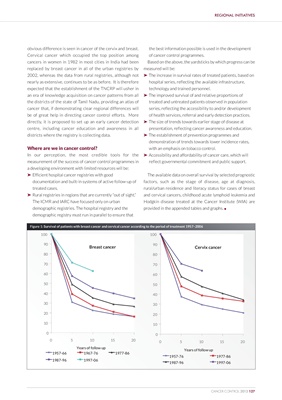
‰ Efficient hospital cancer registries with good The available data on overall survival by selected prognostic
documentation and built-in systems of active follow-up of factors, such as the stage of disease, age at diagnosis,
treated cases. rural/urban residence and literacy status for cases of breast
‰ Rural registries in regions that are currently “out of sight.” and cervical cancers, childhood acute lymphoid leukemia and
The ICMR and IARC have focused only on urban Hodgkin disease treated at the Cancer Institute (WIA) are
demographic registries. The hospital registry and the provided in the appended tables and graphs. l
demographic registry must run in parallel to ensure that
Figure 1: Survival of patients with breast cancer and cervical cancer according to the period of treatment 1957–2006
100 100
90 90
Breast cancer Cervix cancer
80 80
70 70
60 60
50 50
40 40
30 30
20 20
10 10
0 0
0 5 10 15 20 0 5 10 15 20
Years of follow up
Years of follow up
1957-66 1967-76 1977-86
1957-76 1977-86
1987-96 1997-06
1987-96 1997-06
CANCER CONTROL 2013 127